Home > Advocacy & Policy > Policies Affecting GI > Regulatory relief: Prior authorization burdens
Regulatory relief: prior authorization burdens
Prior authorization is a utilization management tool used by payors that requires physicians to obtain preapproval for medical treatments or tests before rendering care to a patient.
AGA position: Reduce prior authorization burdens on physician practices and prevent delays in patient care.
Prior authorization is an administrative hassle for medical practices.
The lengthy approval process typically requires physicians or their staff to spend the equivalent of two business days each week completing prior authorizations — time that could have been spent taking care of patients.
- Nearly 90% of physicians have delayed or avoided prescribing a treatment due to the prior authorization process.
- 94% report that the increased administrative burden has influenced their ability to practice medicine.1
- In Medicare Advantage (MA) plans, physicians are reporting increasingly onerous prior authorization requirements for medical services and procedures that are impacting patient access to medically necessary care.
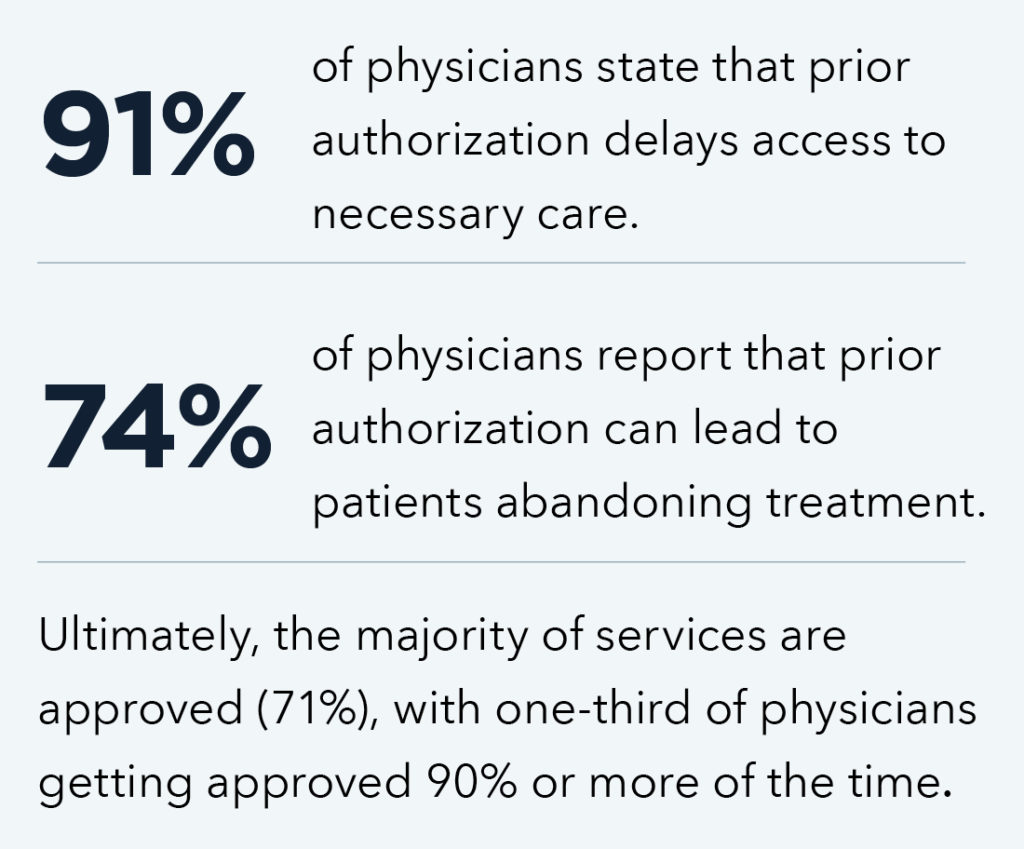
Prior authorization delays care.
This bipartisan legislation aims to increase transparency and accountability of Medicare Advantage plans and streamline the prior authorization process by:
- Establishing an electronic prior authorization process.
- Clarifying the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) authority to establish timeframes for ePA requests.
- Expanding beneficiary protections to improve experiences and outcomes.
- Increasing transparency around MA prior authorization requirements and their use.
- Requiring the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and other agencies to report to Congress on program integrity efforts.
Bottom line: Patients should have timely access to the care their health care providers deem medically necessary — cosponsor the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act.