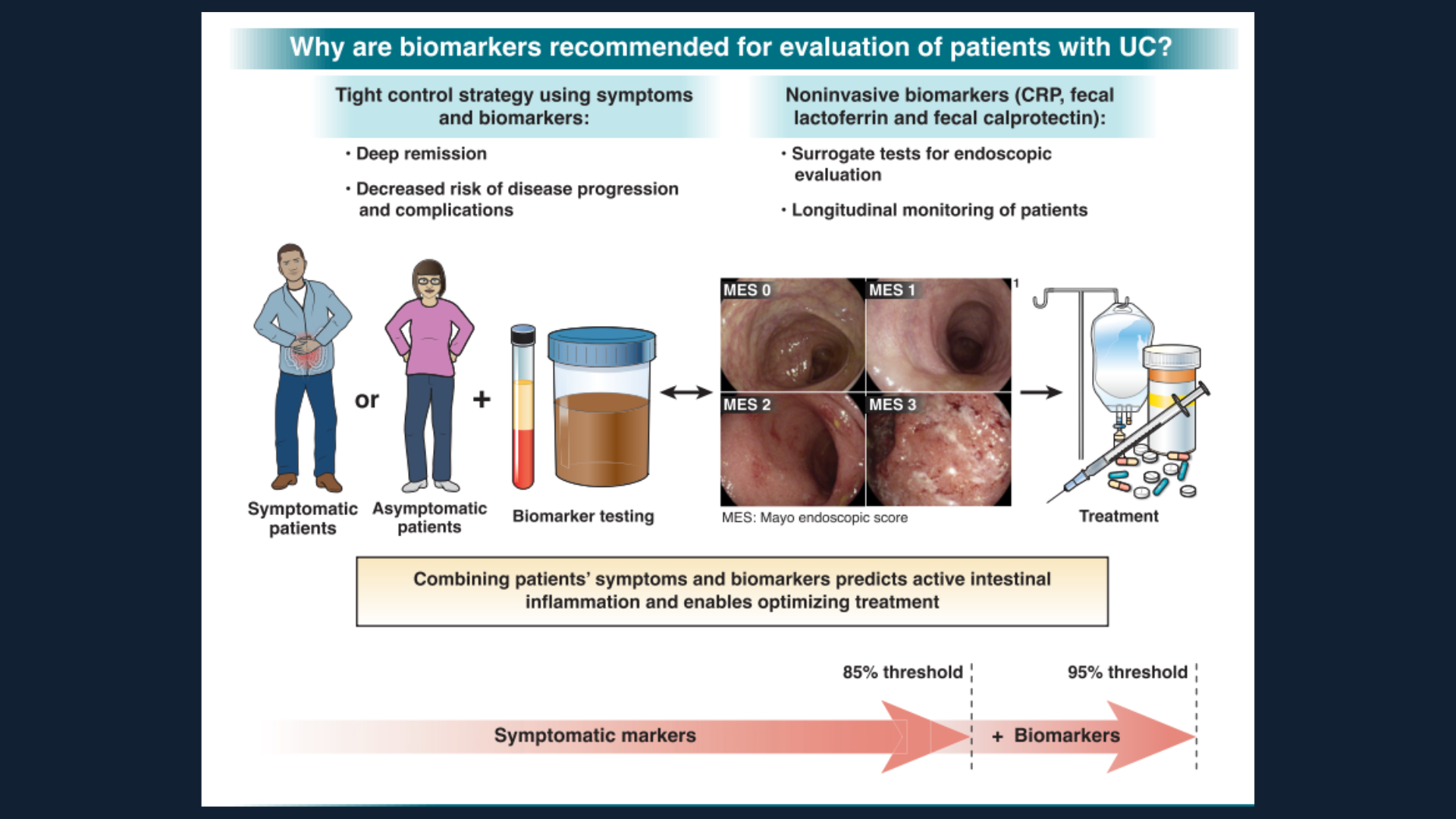
Bethesda, MD (Feb. 21, 2023) — In new evidence-based guidelines, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) recommends non-invasive biomarkers as a first-line strategy for monitoring many patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). These guidelines were published today in Gastroenterology.
The AGA guidelines outline use cases for three biomarkers that provide accurate insights into ulcerative colitis disease activity: serum C-reactive protein (CRP) (blood), fecal calprotectin (stool) and fecal lactoferrin (stool).
“For decades we have regarded endoscopy as the gold standard for monitoring ulcerative colitis and detecting bowel inflammation, but repeated endoscopic assessment is invasive, expensive and often impractical,” says guideline author Siddarth Singh, MD, MS, University of California, San Diego. “Not only are biomarkers accurate, but they provide patients with a cheaper and more convenient option of monitoring to ensure medications are working and ultimately keeping their disease well-managed.”
AGA recommends a monitoring strategy that integrates non-invasive biomarkers for patients with ulcerative colitis in remission (no current symptoms) as well as those with current symptoms.
Patients with ulcerative colitis in symptomatic remission:
- Perform interval biomarker monitoring every six to 12 months.
- AGA recommends stool-based biomarkers over blood testing.
- If biomarkers are normal, AGA suggests continuing biomarker monitoring and avoiding routine endoscopic assessment.
- If biomarkers are elevated, AGA suggests endoscopic assessment by a gastroenterologist.
- Listen to your body! Talk to your doctor about any new symptoms.
Patients with symptomatically active ulcerative colitis:
- Biomarker testing should be the first step to determine the need for endoscopic assessment.
- For patients with mild symptoms who have normal or elevated biomarkers, AGA suggests endoscopic assessment by a gastroenterologist.
- For patients with moderate to severe symptoms who have normal biomarkers, AGA suggests endoscopic assessment by a gastroenterologist.
- For patients with moderate to severe symptoms and elevated biomarkers, AGA suggests treatment adjustment and avoiding endoscopic assessment.
With AGA guidelines guiding the use of noninvasive biomarkers, physicians can confidently offer a more convenient and closer monitoring option for their patients.
“Currently biomarkers are considered experimental by insurers,” adds guideline author Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MBBS, MPH, Massachusetts General Hospital. “This guideline is a major step in showing the value of noninvasive biomarkers and the importance of insurers covering biomarker monitoring to improve patient satisfaction and clinical outcomes.”
AGA will advocate for all insurers to cover the cost of biomarker testing in ulcerative colitis.
About ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is one of the two main types of inflammatory bowel diseases and is more common than Crohn’s disease. It causes inflammation (swelling) and sores (called ulcers) in the large intestine (colon and rectum) and may affect part or all the large intestines. Ulcerative colitis can happen at any age, but it is more likely to develop in people between the ages of 15 and 30, or older than 60 years of age. Learn more in the AGA GI Patient Center.
Resources
Biomarkers in ulcerative colitis guideline
Spotlight (one-page infographic)
Clinical decision support tool
# # #
Media contact: Courtney Reed, media@gastro.org, 301-272-0025
About the AGA Institute
The American Gastroenterological Association is the trusted voice of the GI community. Founded in 1897, the AGA has grown to more than 16,000 members from around the globe who are involved in all aspects of the science, practice and advancement of gastroenterology. The AGA Institute administers the practice, research and educational programs of the organization. www.gastro.org.
AGA is now on Instagram.
Like AGA on Facebook.
Follow us on Twitter @AmerGastroAssn.
Check out our videos on YouTube.
Follow AGA on LinkedIn.
About Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology is the most prominent journal in the field of gastrointestinal disease. As the official journal of the AGA Institute, Gastroenterology delivers up-to-date and authoritative coverage of both basic and clinical gastroenterology. Regular features include articles by leading authorities and reports on the latest treatments for diseases. Original research is organized by clinical and basic-translational content, as well as by alimentary tract, liver, pancreas, and biliary content. www.gastrojournal.org