Search Results for: probiotics – Page 5

Management of pouchitis and inflammatory pouch disorders
1. In patients with ulcerative colitis who undergo IPAA, the AGA makes no recommendation in favor of, or against, the use of probiotics for primary prevention of pouchitis. 2. In patients with ulcerative colitis who undergo IPAA, the AGA suggests against using antibiotics for the primary prevention of pouchitis. 3. In patients with ulcerative […]
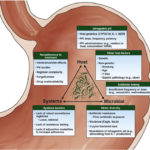
Management of refractory helicobacter pylori infection
[…] with patient demographic and clinical factors (including prior non-H. pylori antibiotic exposure) is important. Aggregated data should be made publicly available to guide local selection of H. pylori eradication therapy. 12. Proposed adjunctive therapies, including probiotics, are of unproven benefit as treatment for refractory H. pylori infection, and thus, their use should be considered experimental.

Medical management of microscopic colitis
[…] suggests against treatment with Boswellia serrata over no treatment for the induction of clinical remission. 8. In patients with symptomatic microscopic colitis, AGA suggests against treatment with probiotics over no treatment for the induction of clinical remission. 9. In patients with recurrence of symptoms following discontinuation of induction therapy for microscopic colitis, AGA recommends […]
Medical management of colonic diverticulitis
[…] understand that approximately 50% of the risk for diverticulitis is attributable to genetic factors. 11. Patients with a history of diverticulitis should not be treated with mesalamine, probiotics or rifaximin to prevent recurrent diverticulitis. 12. Patients should be educated that complicated diverticulitis is most often the first presentation of diverticulitis. The risk of complicated […]
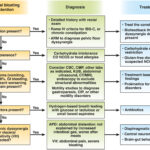
Evaluation and management of belching, abdominal bloating and distention
[…] out a pelvic floor disorder. 9. When dietary modifications are needed (e.g., low-fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols diet), a gastroenterology dietitian should preferably monitor treatment. 10. Probiotics should not be used to treat abdominal bloating and distention. 11. Biofeedback therapy may be effective for bloating and distention when a pelvic floor disorder is […]
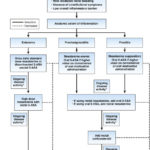
Management of mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
[…] 5-ASA, regardless of disease extent, AGA suggests adding either oral prednisone or budesonide MMX. 11. In patients with mild–moderate UC, AGA makes no recommendation for use of probiotics. 12. In patients with mild–moderate UC despite 5-ASA therapy, AGA makes no recommendation for use of curcumin. 13. In patients with mild–moderate UC without Clostridium difficile […]
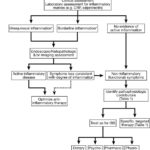
Functional gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
[…] chronic diarrhea in quiescent IBD. 9. Antispasmodics, neuropathic-directed agents, and anti-depressants should be used for functional pain in IBD while use of opiates should be avoided. 10. Probiotics may be considered for treatment of functional symptoms in IBD. 11. Pelvic floor therapy should be offered to IBD patients with evidence of an underlying defecatory […]
Risks and benefits of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
[…] PPIs should be periodically reevaluated so that the lowest effective PPI dose can be prescribed to manage the condition. 7. Long-term PPI users should not routinely use probiotics to prevent infection. 8. Long-term PPI users should not routinely raise their intake of calcium, vitamin B12 or magnesium beyond the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA). 9. […]
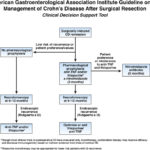
Management of Crohn’s disease after surgical resection
[…] (anti-TNF) therapy and/or thiopurines over other agents. 3. In patients with surgically induced remission of Crohn’s disease, AGA suggests against using mesalamine (or other 5-aminosalicylates), budesonide or probiotics. 4. In patients with surgically induced remission of Crohn’s disease receiving pharmacological prophylaxis, AGA suggests postoperative endoscopic monitoring at 6 to 12 months after surgical resection […]
Management of acute diverticulitis
[…] use of nonaspirin NSAIDs if possible. 8. AGA recommends against the use of mesalamine after acute uncomplicated diverticulitis. 9. AGA suggests against the use of rifaximin after acute uncomplicated diverticulitis. 10. AGA suggests against the use of probiotics after acute uncomplicated diverticulitis. 11. AGA suggests advising patients with diverticular disease to consider vigorous physical activity.