Gastroenterology
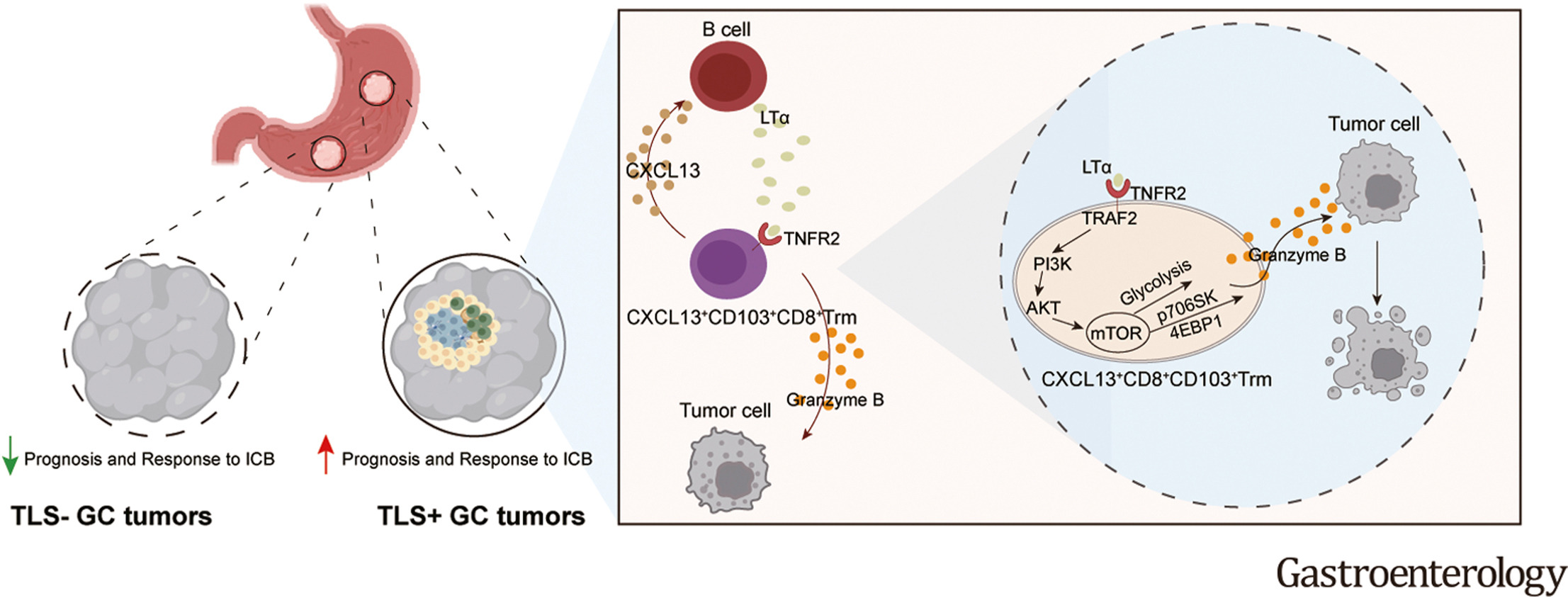
This study further reveals a crucial role for cellular communication between TLS-associated B cell and CXCL13+CD103+CD8+ Trm cells in antitumor immunity, providing valuable insights into the potential use of the lymphotoxin-α/TNFR2 axis within CXCL13+CD103+CD8+ Trm cells for advancing immunotherapy strategies in gastric cancer.
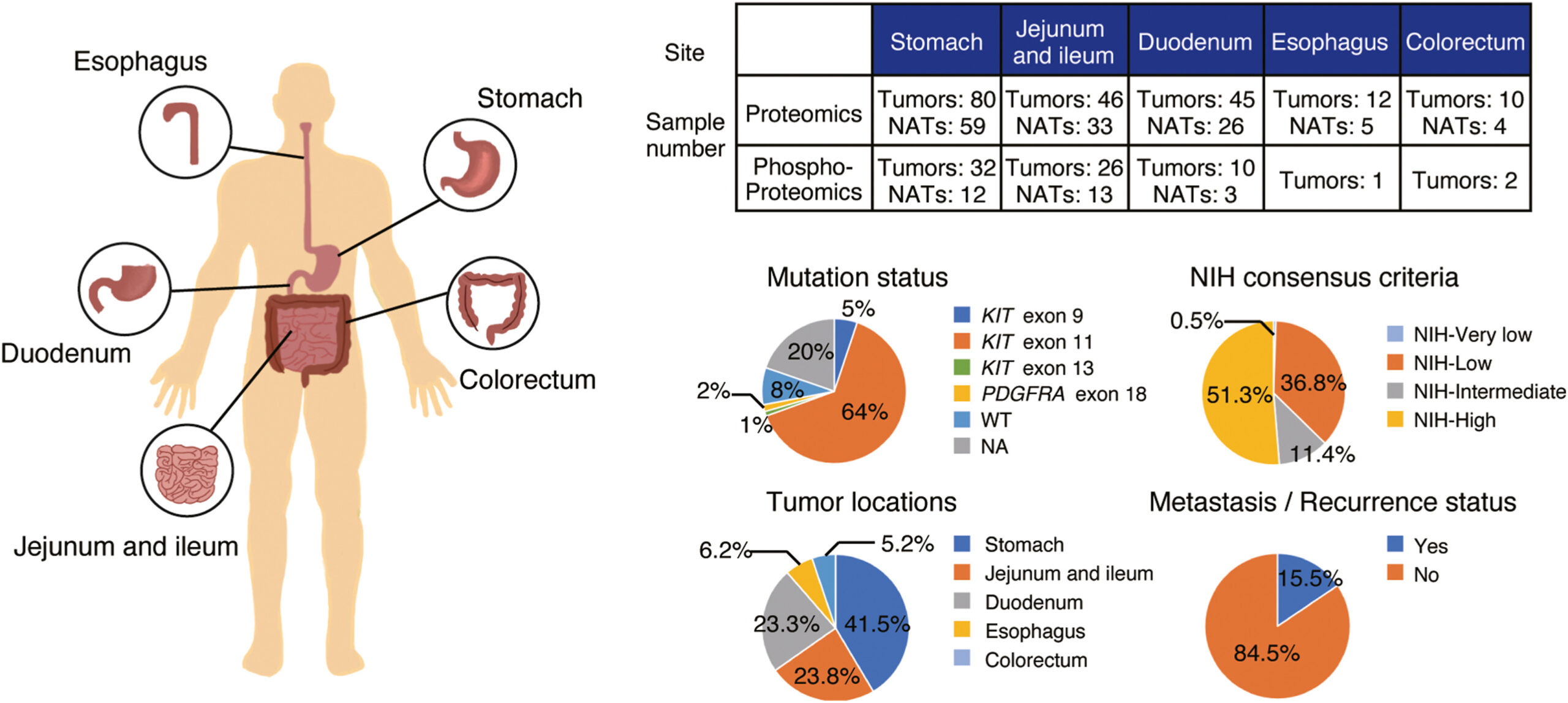
Our study provides a valuable data resource and highlights potential therapeutic approaches for GIST.
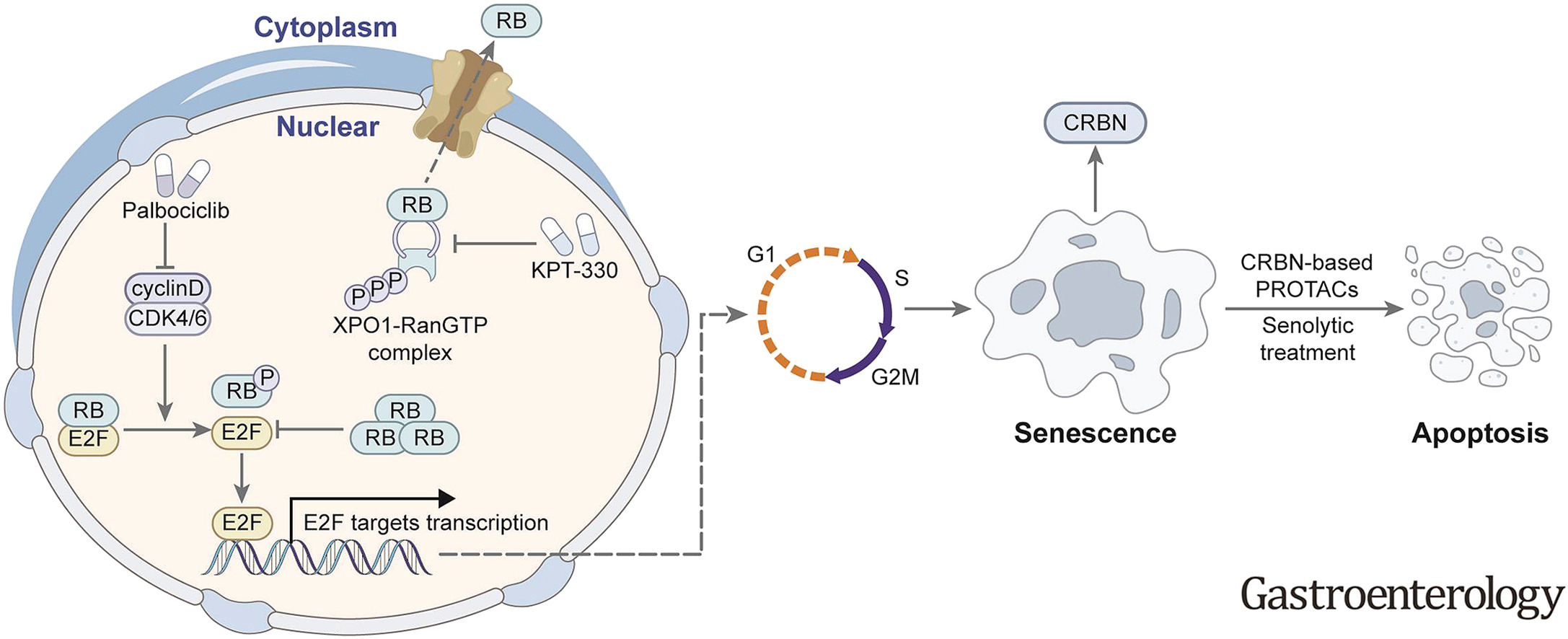
Our study demonstrates a striking synergy in senescence induction of liver cancer cells through the combination of CDK4/6 inhibitor and XPO1 inhibitor. These findings also shed light on the molecular processes underlying the vulnerability of senescent liver cancer cells to CRBN-based PROTAC therapy.
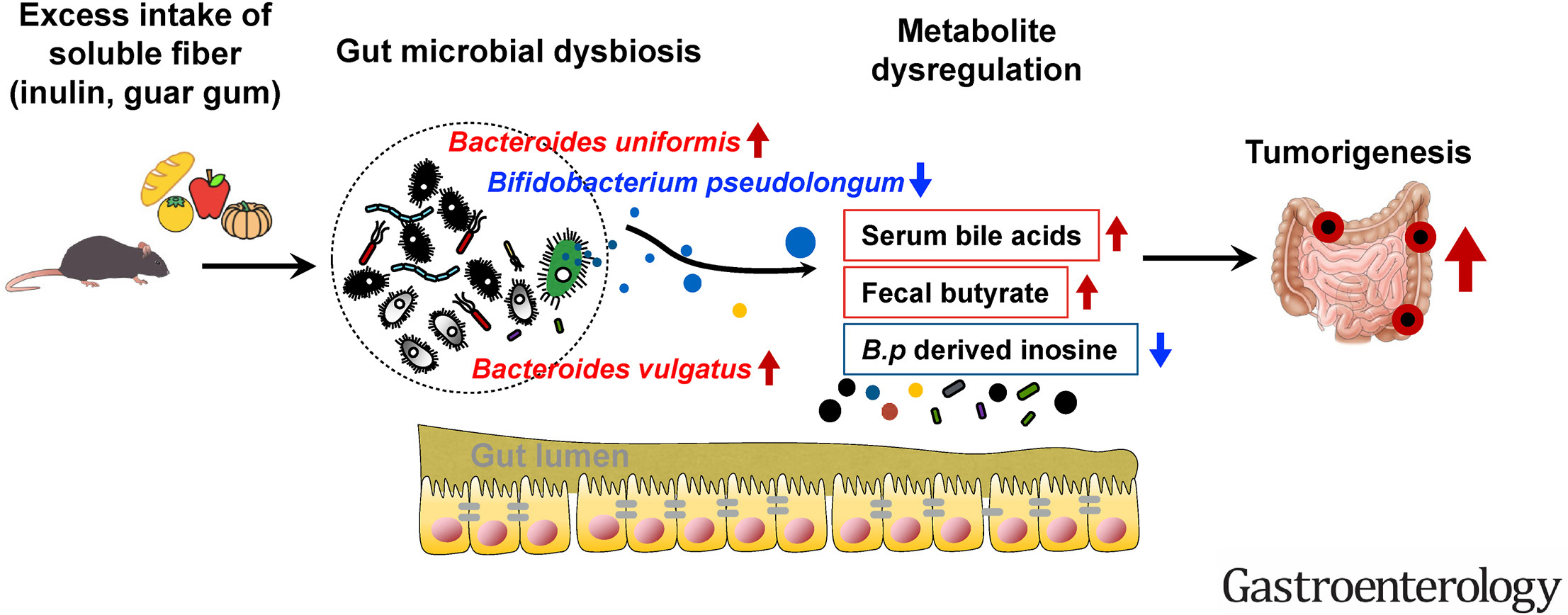
High-dose soluble but not insoluble fiber potentiates colorectal tumorigenesis in a dose-dependent manner by dysregulating gut microbiota and metabolites in mice.
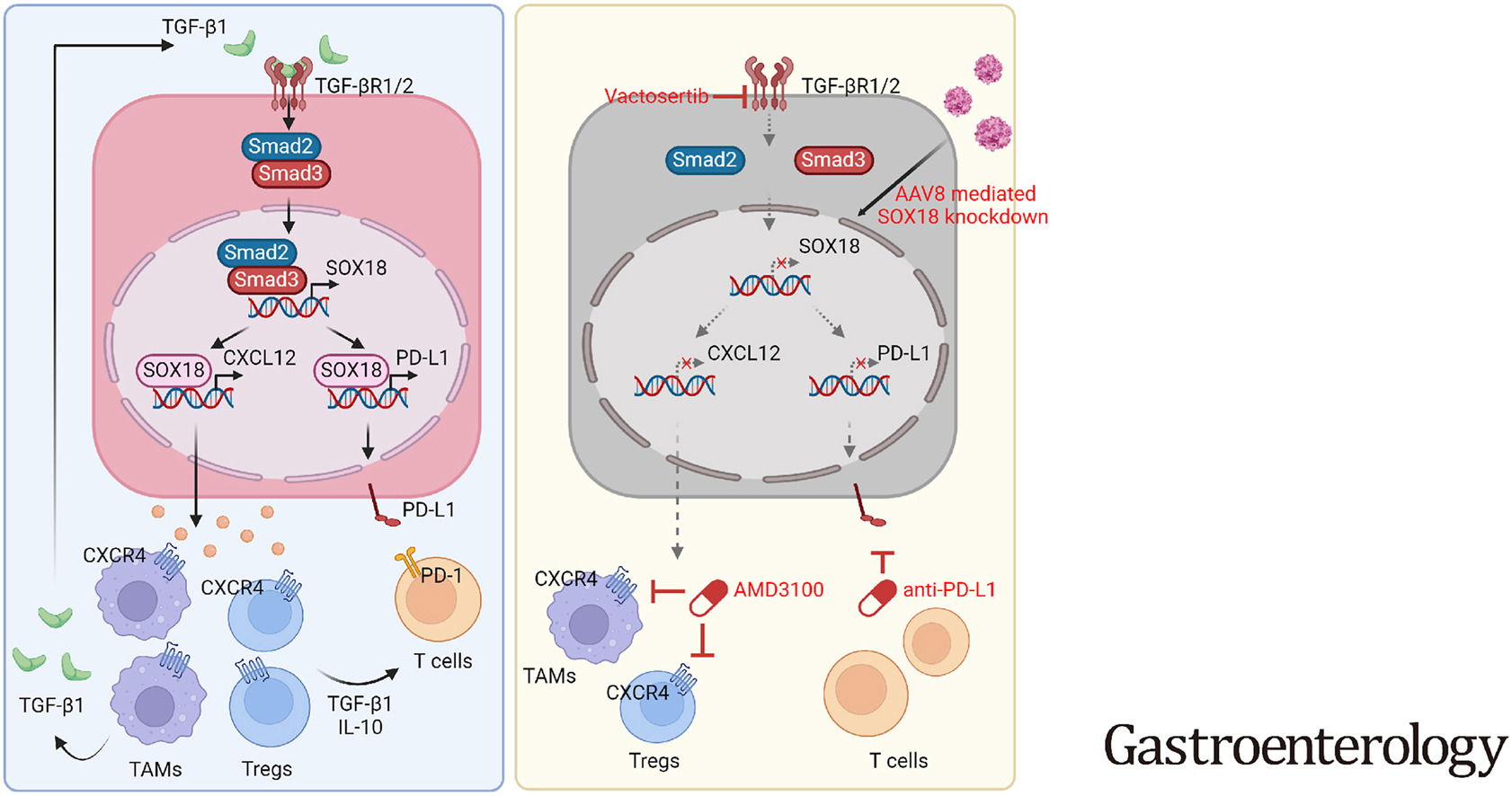
SOX18 promoted the accumulation of immunosuppressive TAMs and Tregs in the microenvironment by transactivating CXCL12 and PD-L1. CXCR4 inhibitor or TGFβR1 inhibitor in synergy with anti-PD-L1 represented a promising combination strategy to suppress HCC progression and metastasis.
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology (CMGH)
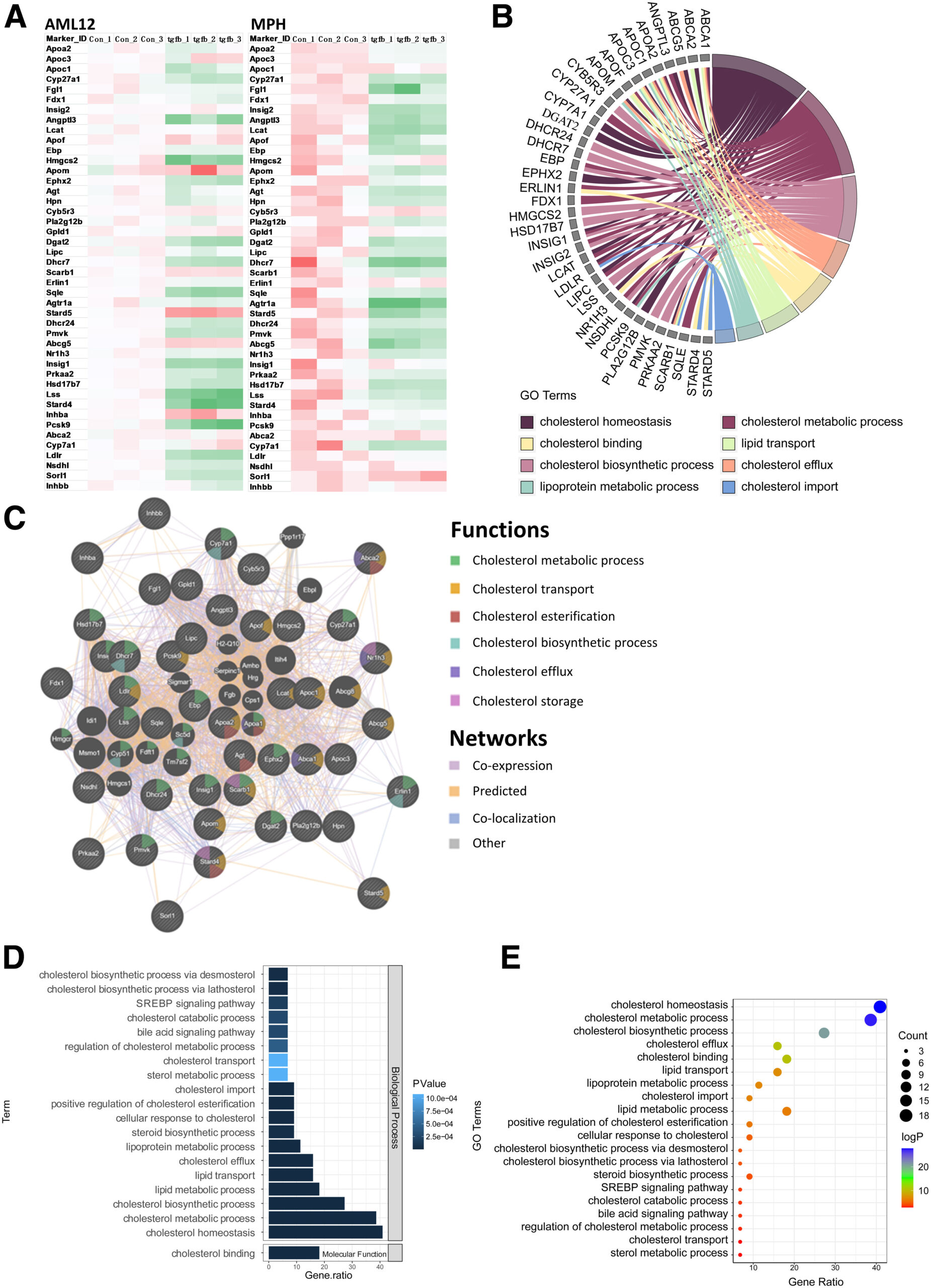
TGF-β1 inhibits cholesterol metabolism whereas cholesterol attenuates TGF-β1 downstream effects in hepatocytes.
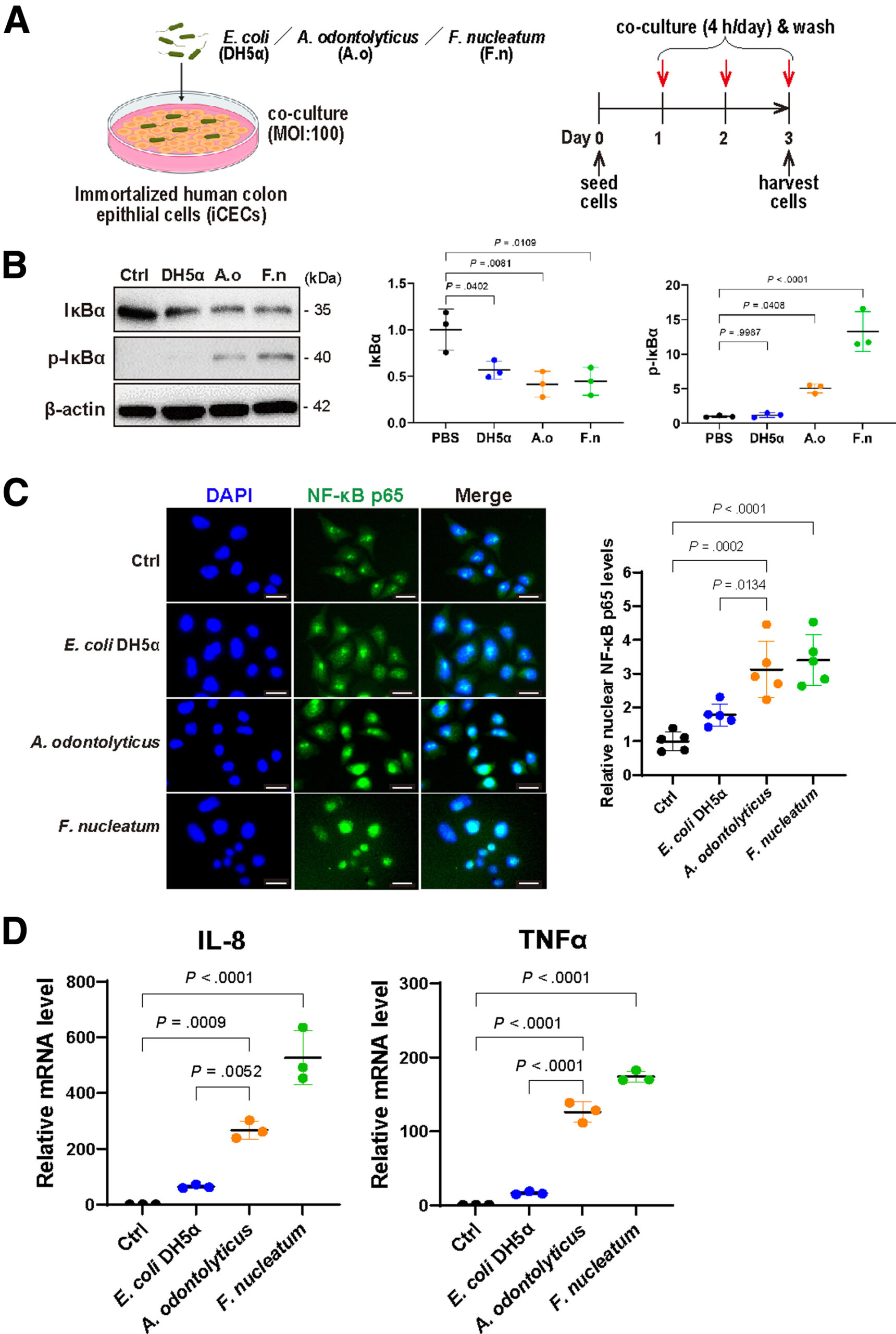
A odontolyticus secretes MVs, which cause chronic inflammation and ROS production in colonic epithelial cells, leading to the initiation of CRC.
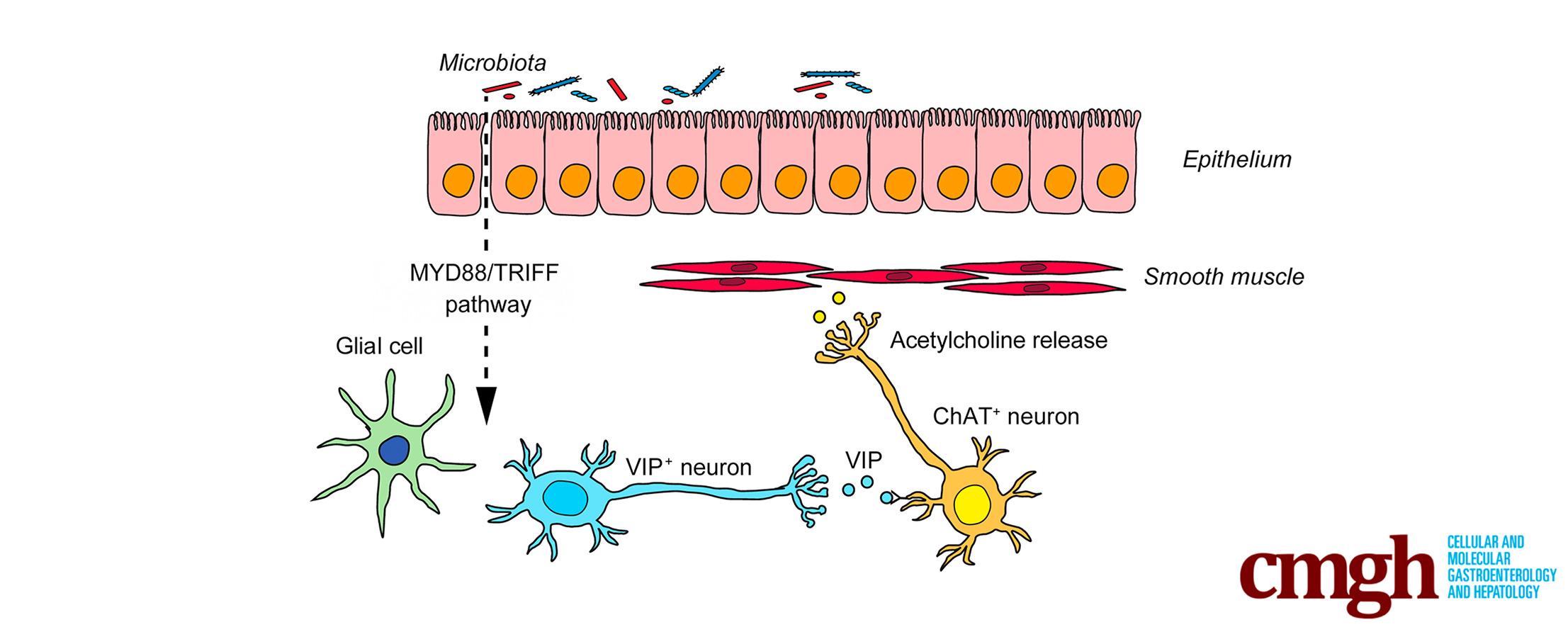
Microbial control of gastrointestinal motility is both region- and bacteria-specific; it reacts to environmental changes and is mediated by innate immunity-neural system interactions. By regulating cholinergic nerves, small intestinal VIP plays a key role in this process, thus providing a new therapeutic target for patients with motility disorders.
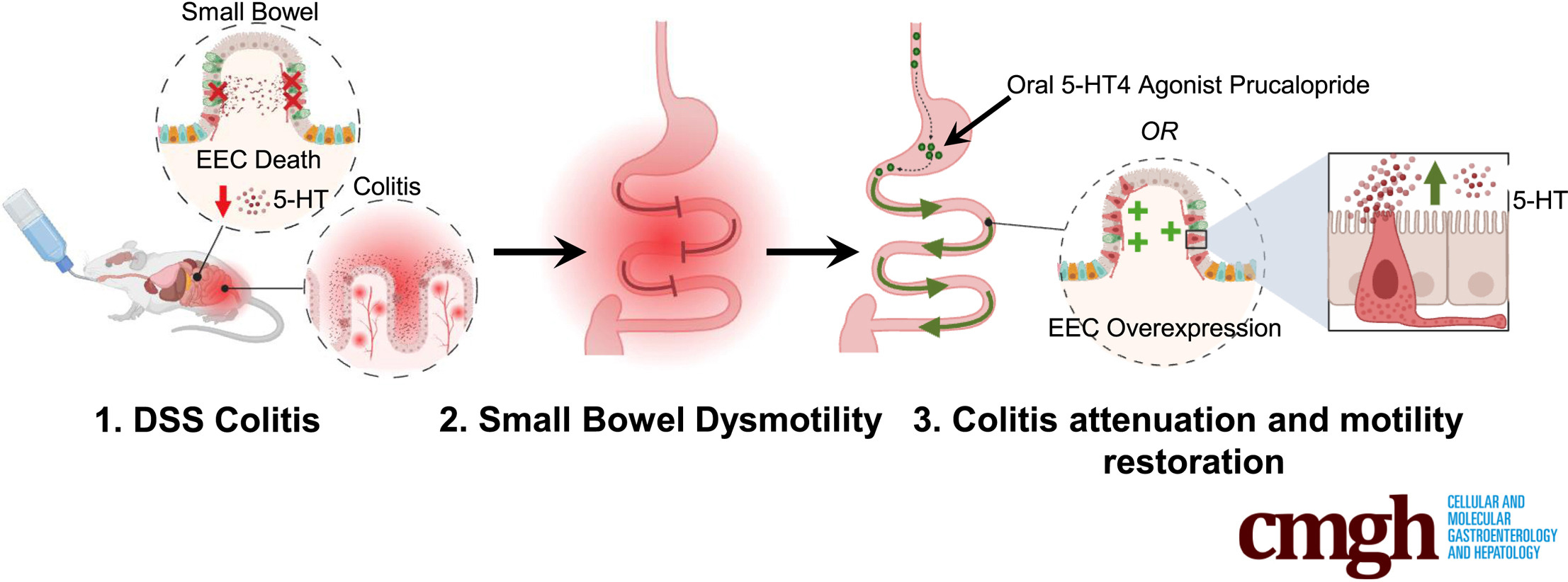
Experimental DSS colitis induces significant small-bowel dysmotility in mice owing to enteroendocrine loss that can be reversed by genetic modulation of EEC or administering serotonin analogs, suggesting novel therapeutic approaches for patients with symptomatic colitis.
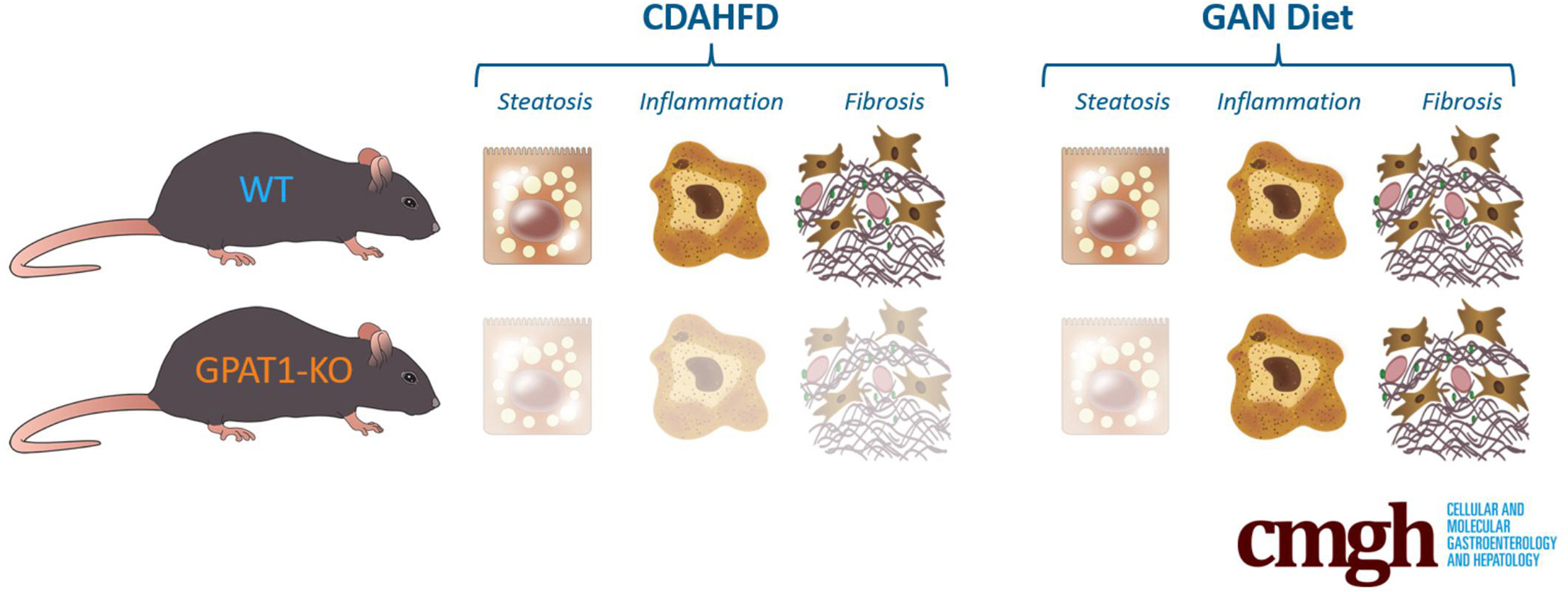
Our preclinical data support the notion that lipid metabolism pathways regulated by GPAT1 in hepatocytes play an essential role in NASH progression, albeit in a model-dependent manner.
Gastro Hep Advances (GHA)
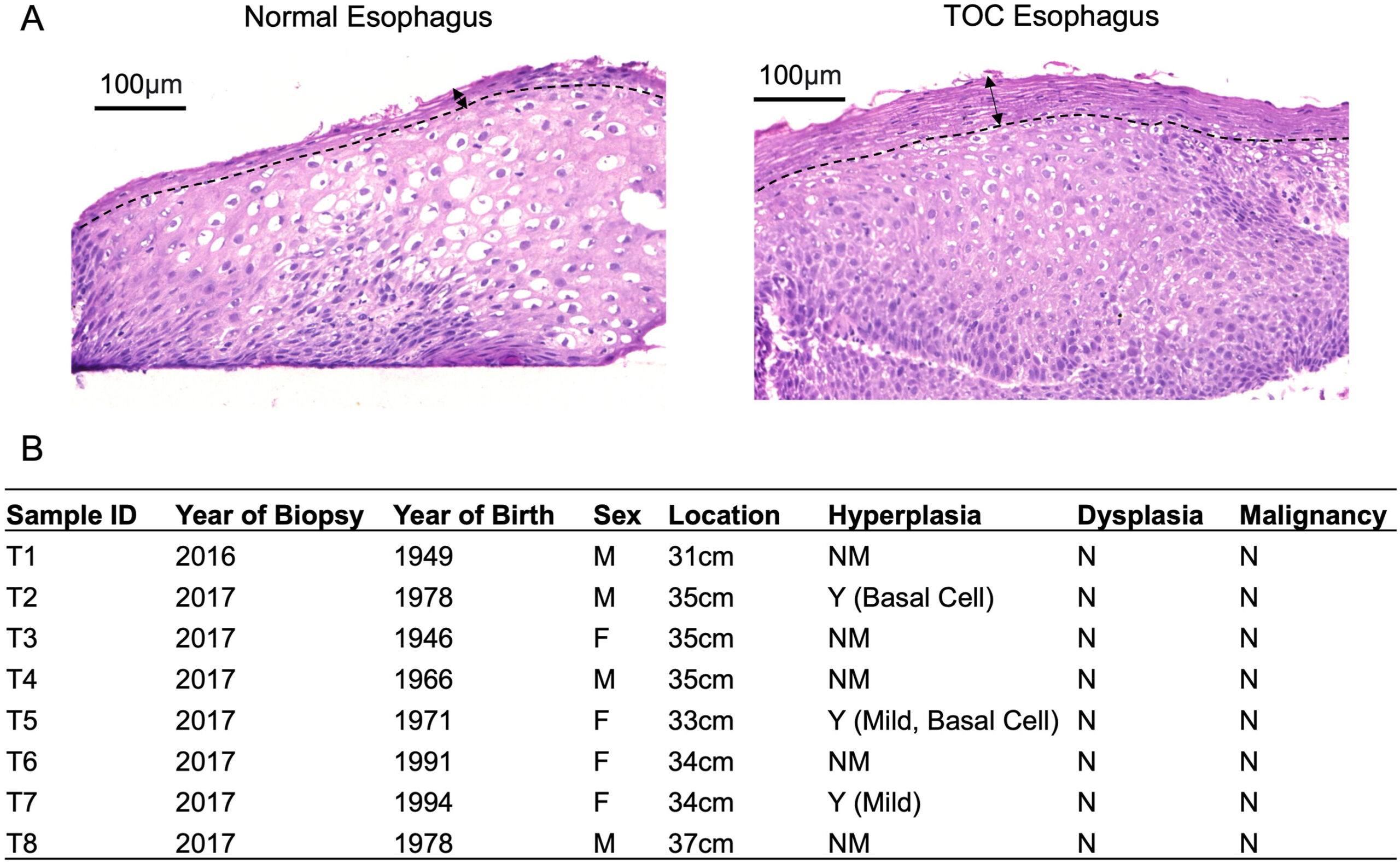 Transcriptional changes occur in TOC esophagus prior to the onset of dysplasia, many of which are associated with ESCC. These findings support the utility of TOC to help reveal the early molecular processes that lead to sporadic ESCC.
Transcriptional changes occur in TOC esophagus prior to the onset of dysplasia, many of which are associated with ESCC. These findings support the utility of TOC to help reveal the early molecular processes that lead to sporadic ESCC.
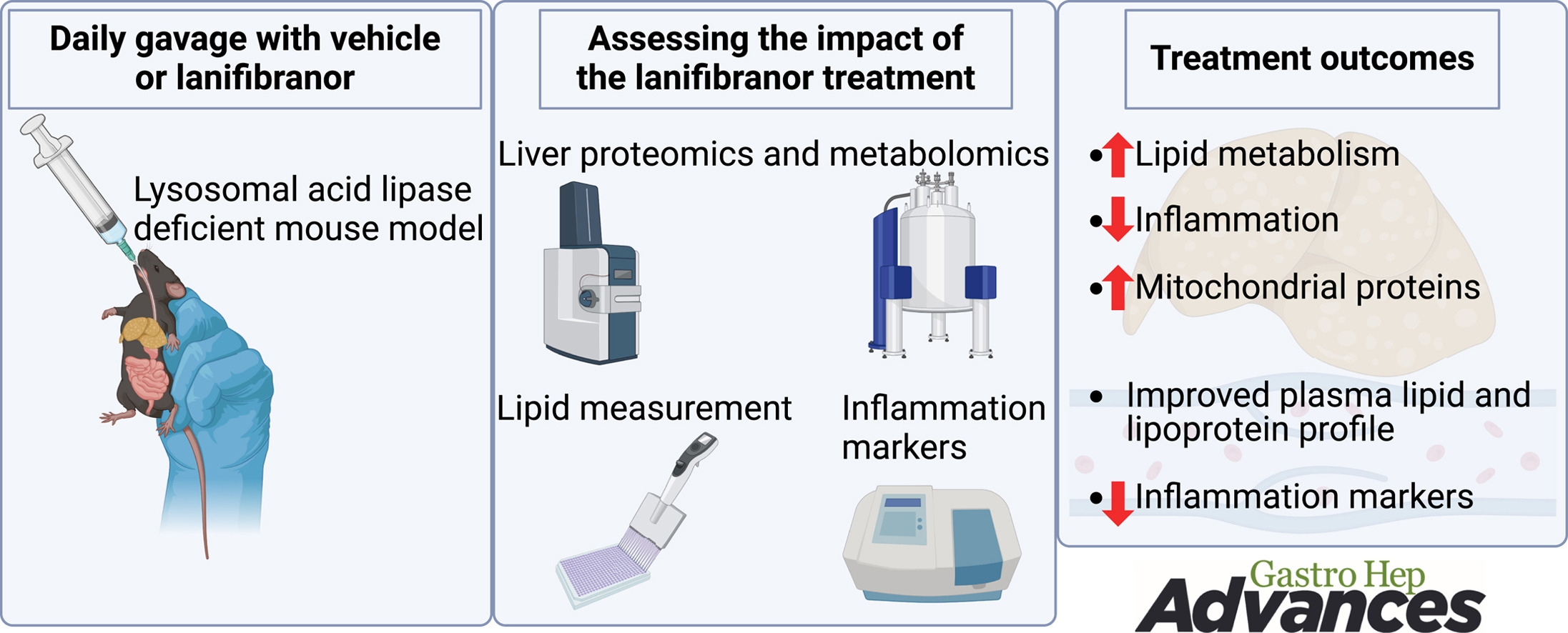
Lanifibranor treatment positively affected liver inflammation and dyslipidemia in Lal−/− mice. These findings suggest the necessity of a further combined study of lanifibranor with enzyme replacement therapy in Lal−/− mice to improve the phenotype. Moreover, there is a compelling rationale for conducting clinical trials to assess the efficacy of lanifibranor as a potential treatment option for LAL-D in humans.
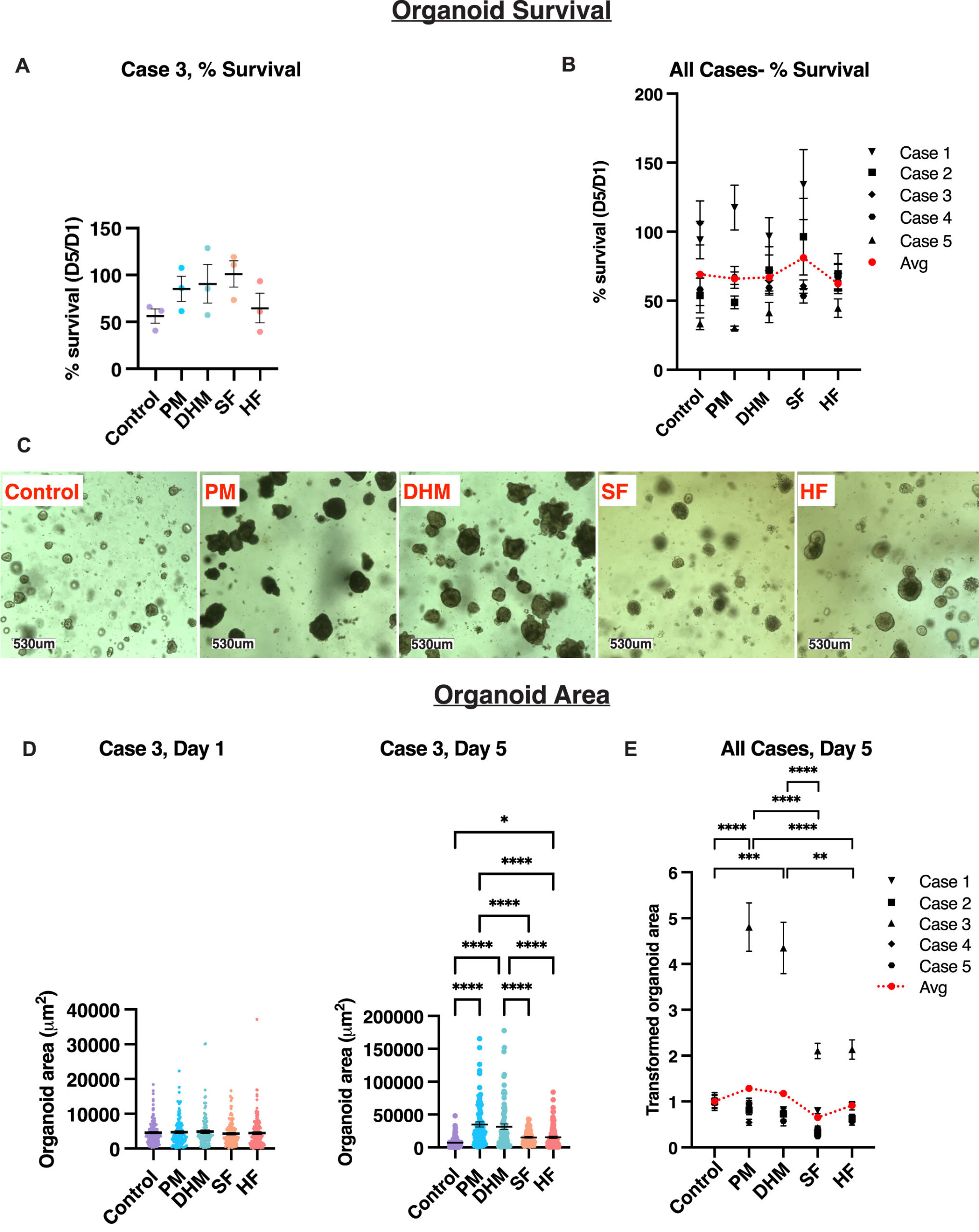
Our results demonstrate that parental milk, and to a lesser extent donor human milk, support robust intestinal epithelial proliferation, differentiation, and homeostatic cytokine production, suggesting a critical role for factors enriched in human milk in intestinal epithelial health.
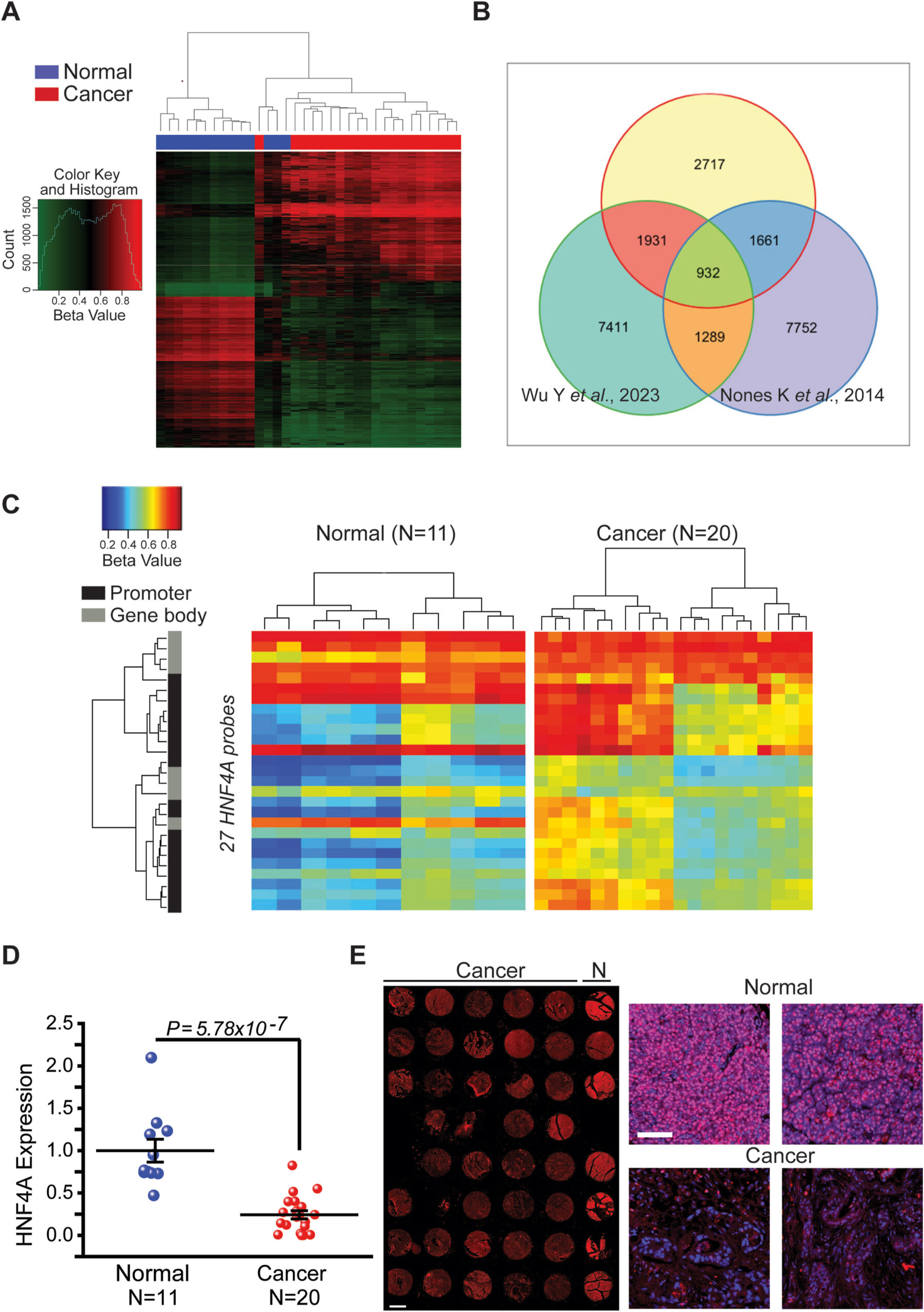
HNF4A silencing, mediated by promoter DNA methylation, drives pancreatic cancer development and aggressiveness leading to poor patient survival.
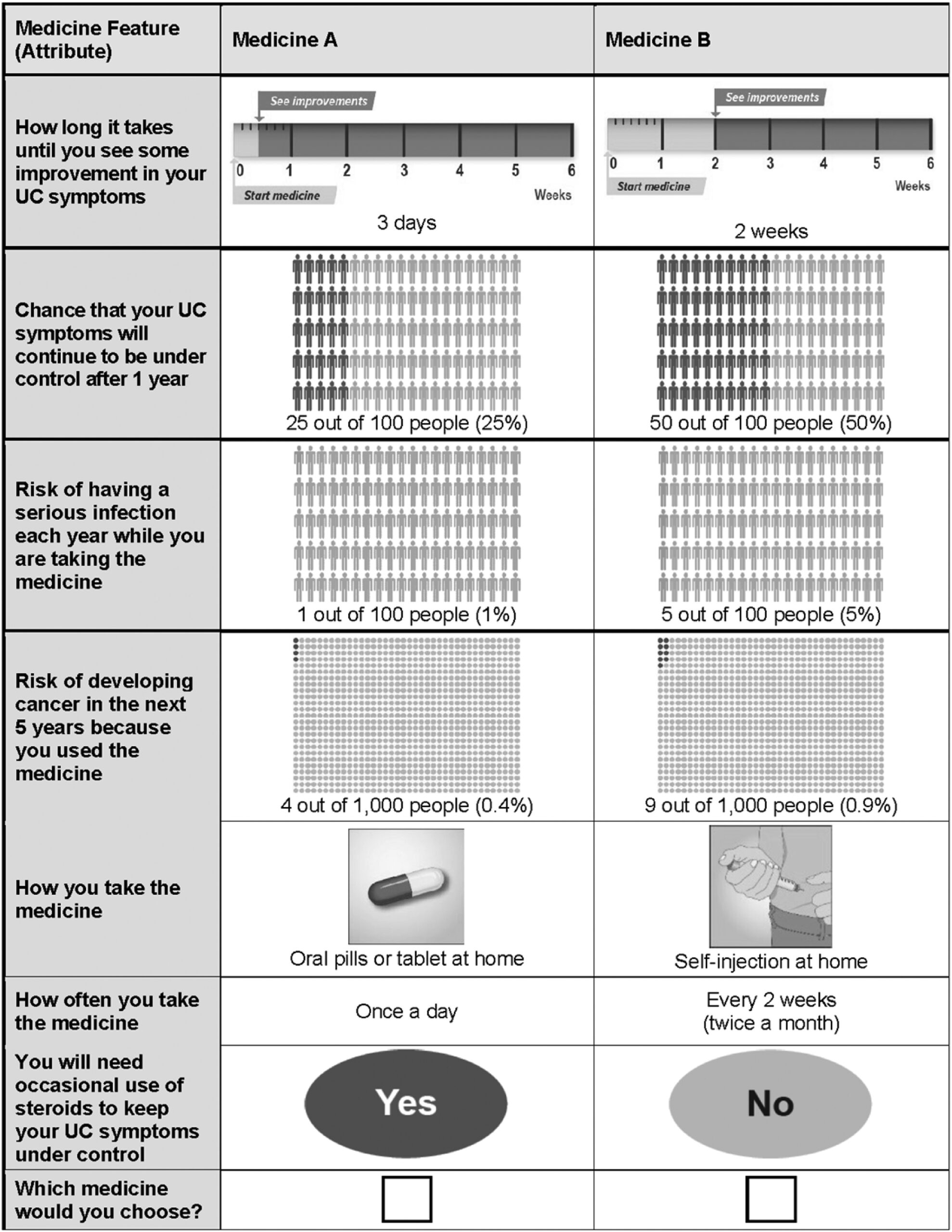
Of the attributes evaluated, individuals with UC in Middle Eastern countries most value avoiding five-year risk of malignancy and a higher probability of symptom control, on average.