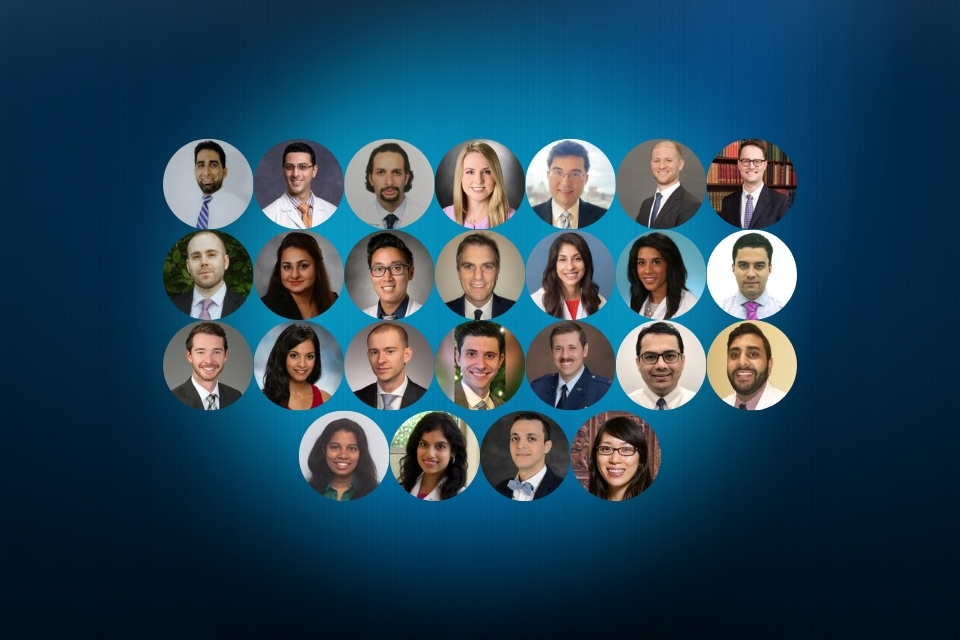
Each year during Digestive Disease Week®, AGA hosts a session titled “Advancing Clinical Practice: GI Fellow-Directed Quality-Improvement Projects.” This year 25 quality improvement (QI) initiatives were selected — you can review these abstracts in the August issue of Gastroenterology in the “AGA Section” or review a presenter’s abstract by clicking their image. Kudos to the promising fellows featured below, who all served as lead authors for their QI projects.
My AGA
AGA Journals
AGA University
AGA Research Foundation
AGA Job Board
My AGA

My AGA
Make the most of your AGA membership. Access your AGA profile, event registrations, member directory and more.
AGA Journals
AGA Journals
AGA’s peer-reviewed journals offer high-quality research on current advances in GI and hepatology: Gastroenterology, CGH, CMGH, TIGE and Gastro Hep Advances.
AGA University
AGA University
AGA University is your home for in-person meetings, webinars and other educational tools designed to help you stay current with advances in the GI field and earn MOC/CME.
AGA Research Foundation

AGA Research Foundation
The AGA Research Foundation funds young investigators who are committed to advancing gastroenterology. Through research, we can identify new treatment options for digestive disease patients.
AGA Job Board
AGA Job Board
AGA’s official job board, GICareerSearch.com, features new job postings daily. Employers can also post open positions.
MENUMENU
- Clinical Guidance
-
-

Clinical Guidance
Our clinical guidelines and updates help you make the best evidence-based decisions for your patients.
-
-
- Journals & Publications
-
-

Male doctor reading medical record while sitting at desk. Confident healthcare worker is working in his office. He is wearing lab coat in clinic. Journals & Publications
Latest research and ideas from the GI field.
-
- GastroenterologyThe premier journal in GI.
- Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology (CGH)The go-to resource in clinical GI.
- Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology (CMGH)Impactful digestive biology research.
- Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (TIGE)Cutting-edge advances in GI endoscopy.
-
-
- Meetings & Learning
-
-

Speaker giving a talk in conference hall at business event. Audience at the conference hall. Business and Entrepreneurship concept. Meetings & Learning
Earn CME, MOC and improve your skills.
-
-
- News
- Membership
-
-

High angle shot of a team of doctors using a digital tablet together Membership
More than 16,000 professionals worldwide call AGA their professional home.
-
-
MENUMENU
- DDW
- Practice Resources
-
-

a medical salesman or administrator is sitting with a female doctor and running through a presentation . He is explaining something and referring to the computer screen in front of them on the desk. Practice Resources
Tools to maximize efficiency and help you deliver high-quality care.
-
- Practice ToolsCutting-edge resources to improve your patient care.
- New Technology & TechniquesThe latest innovations in GI.
- Quality & Performance MeasuresSupport to meet reporting requirements.
- ReimbursementTools to understand policies and advocate for reimbursement.
- GI Patient CenterBy specialists, for patients.
-
-
- Research & Awards
-
-

Shot of a female scientist in a laboratory working with a microscope. Research & Awards
Funding opportunities and other initiatives advancing discovery.
-
-
-
-
- Fellows & Early Career
-
-

Shot of a diverse team of doctors having a discussion Fellows & Early Career
Resources designed for early career gastroenterologists.
-
-