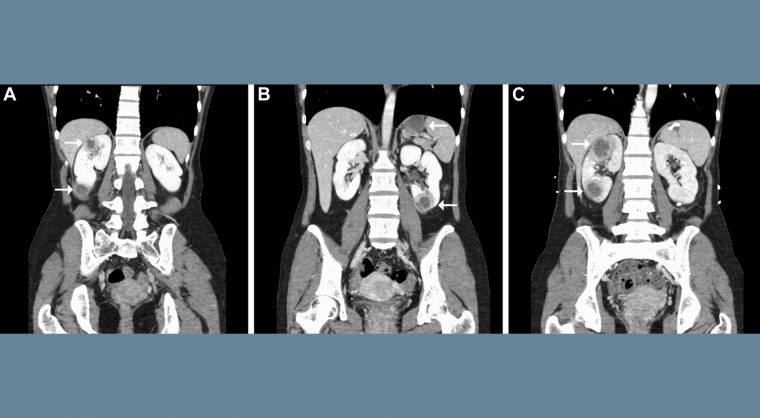
Gastroenterology image challenge: A 41-year-old woman with a history of ulcerative colitis and pyoderma gangrenosum presented with a two-day history of fever and back pain on the left side. She was previously treated with prednisone (9 mg/day), azathioprine (50 mg/day), mesalazine (4800 mg/day) and infliximab (every eight weeks). The patient was diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis due to Klebsiella aerogenes, and treatment with levofloxacin was initiated. A week later, computed tomography of the abdomen revealed bilateral multifocal renal abscesses and a splenic abscess (figures A and B). Suspecting levofloxacin-resistant organisms, her antimicrobial treatment was changed from levofloxacin to meropenem on admission. Interventional radiology–guided drainage was performed for the renal abscess; however, the microbiological findings were unremarkable. Cytological analysis of renal and splenic abscess showed neutrophil-dominant inflammatory cells with no microorganisms. Despite intervention and empiric antimicrobials, including levofloxacin followed by a two-month course of meropenem, her abscesses increased in size (figure C).
What is the diagnosis?
To find out the diagnosis, read the full case in Gastroenterology.