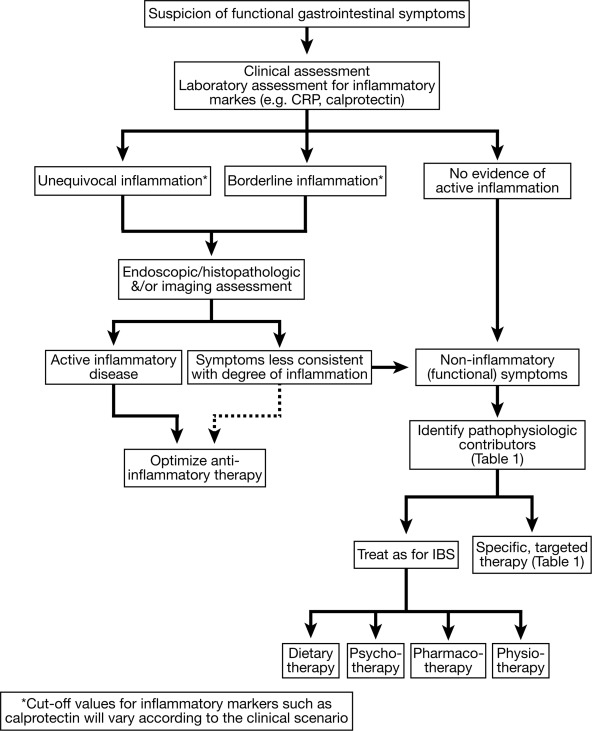
1. A stepwise approach to rule-out ongoing inflammatory activity should be followed in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients with persistent GI symptoms (measurement of fecal calprotectin, endoscopy with biopsy, cross-sectional imaging).
2. In those patients with indeterminate fecal calprotectin levels and mild symptoms, clinicians may consider serial calprotectin monitoring to facilitate anticipatory management.
3. Anatomic abnormalities or structural complications should be considered in patients with obstructive symptoms including abdominal distention, pain, nausea and vomiting, obstipation or constipation.
4. Alternative pathophysiologic mechanisms should be considered and evaluated (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, bile acid diarrhea, carbohydrate intolerance, chronic pancreatitis) based on predominant symptom patterns.
5. A low fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAP) diet may be offered for management of functional GI symptoms in IBD with careful attention to nutritional adequacy.
6. Psychological therapies (cognitive behavioral therapy, hypnotherapy, mindfulness therapy) should be considered in IBD patients with functional symptoms.
7. Osmotic and stimulant laxative should be offered to IBD patients with chronic constipation.
8. Hypomotility agents or bile-acid sequestrants may be used for chronic diarrhea in quiescent IBD.
9. Antispasmodics, neuropathic-directed agents, and anti-depressants should be used for functional pain in IBD while use of opiates should be avoided.
10. Probiotics may be considered for treatment of functional symptoms in IBD.
11. Pelvic floor therapy should be offered to IBD patients with evidence of an underlying defecatory disorder.
12. Until further evidence is available, fecal microbiota transplant should not be offered for treatment of functional GI symptoms in IBD.
13. Physical exercise should be encourage in IBD patients with functional GI symptoms.
14. Until further evidence is available, complementary and alternative therapies should not be routinely offered for functional symptoms in IBD.