Pharmacological management of irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C)
Nine clinical recommendations to guide the use of FDA-approved and over-the-counter medications for irritable bowel syndrome with predominant constipation (IBS-C).
Pharmacological management of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D)

Eight clinical recommendations to guide the use of FDA-approved and over-the-counter medications for irritable bowel syndrome with predominant diarrhea (IBS-D).
Diagnosis and management of cancer risk for gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis syndromes
The U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer (CRC) has 14 recommendations on genetic evaluation, surveillance and treatment best practices.
Systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)

Guideline provides you with the most up-to-date guidance on how to use systemic therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Diagnostic and management strategies for patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Management of Barrett’s esophagus
Answers to your top questions on the diagnosis, key clinical features and management of Barrett’s esophagus.
Diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)

Preferred approaches to the diagnostic, therapeutic and preventive aspects for the care of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
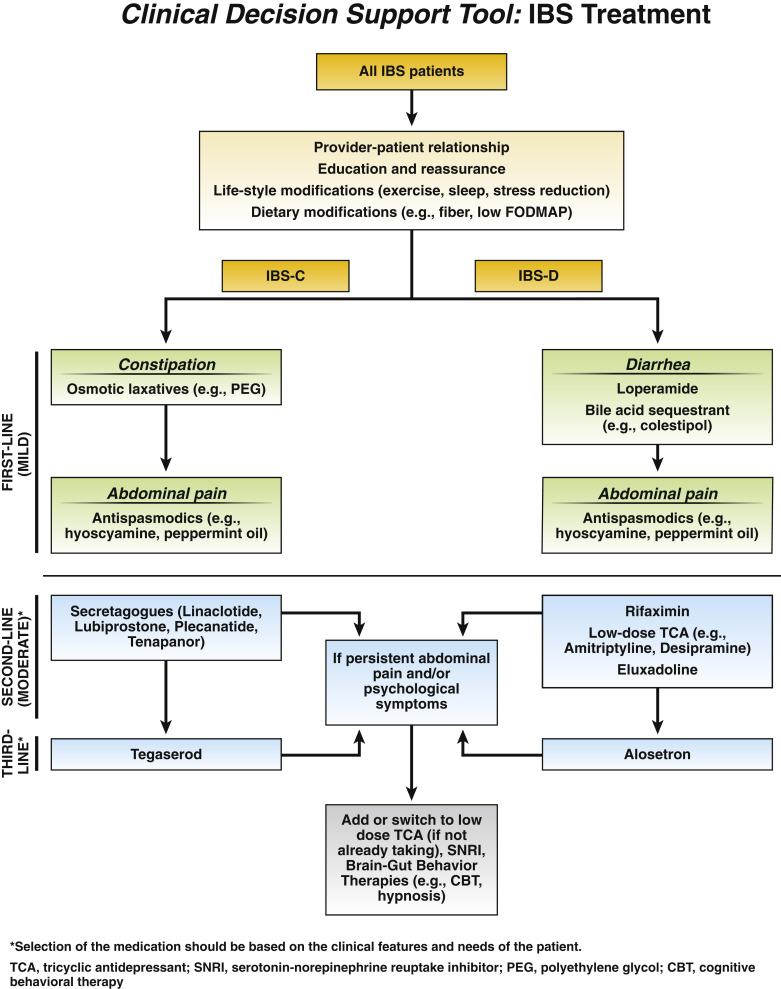
Evaluation and management of constipation
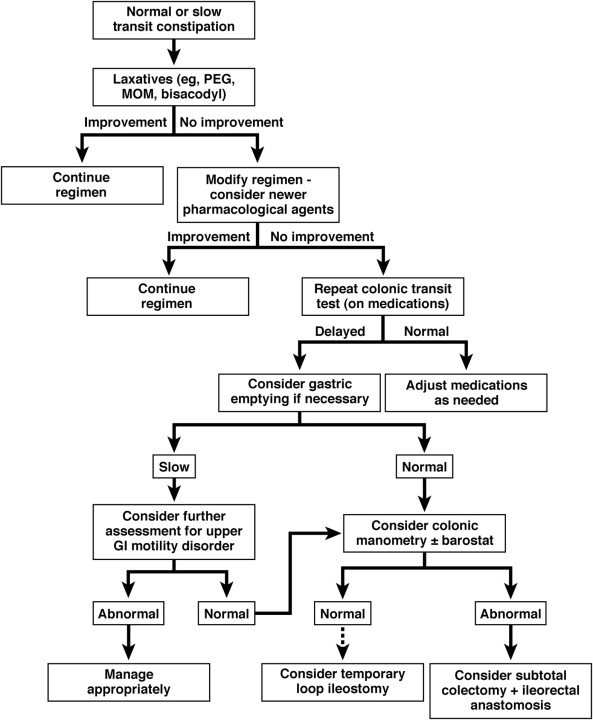
Recommendations for the assessment and therapeutic treatment of constipation.
Use of thiopurines, methotrexate and anti–TNF-α biologic drugs for the induction and maintenance of remission in inflammatory Crohn’s disease
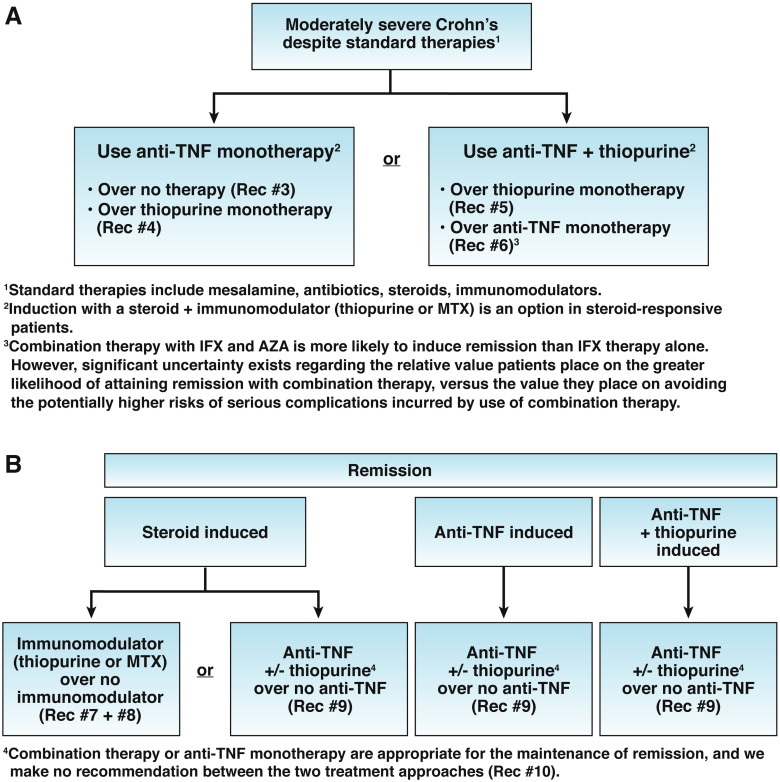
A guide to choosing the best drugs for the induction and maintenance of remission in inflammatory Crohn’s disease.
Genetic evaluation and management of Lynch syndrome
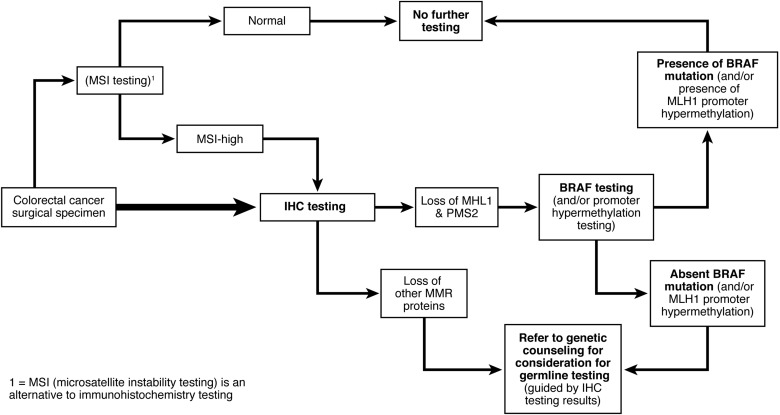
Guidance from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer (CRC) on the appropriate provision of genetic testing and management of patients at risk for and affected with Lynch syndrome, the most common cause of inherited CRC.