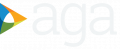Gastroenterology image challenge: A 16-year-old girl with a 2-year history of ulcerative colitis (UC) was referred to a university hospital because of fever, vomiting and epigastric pain for 10 days; bloody diarrhea during the last month; and a rapid involuntary weight loss (5 kg). Sixth months earlier, during remission with oral mesalamine (60 mg/kg), she suffered a mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis flare-up requiring oral prednisolone (1 mg/kg for 2 weeks and then tapered). At admission, physical examination showed pallor, mild signs of dehydration and diffuse abdominal pain without signs of peritoneal irritation. Written consent for publication was obtained from the patient and her parents.
Laboratory investigations revealed anemia, mild eosinophilia, hypoalbuminemia, an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate and fecal calprotectin. Specific serologic tests and blood and stool cultures for bacteria and viruses were negative.
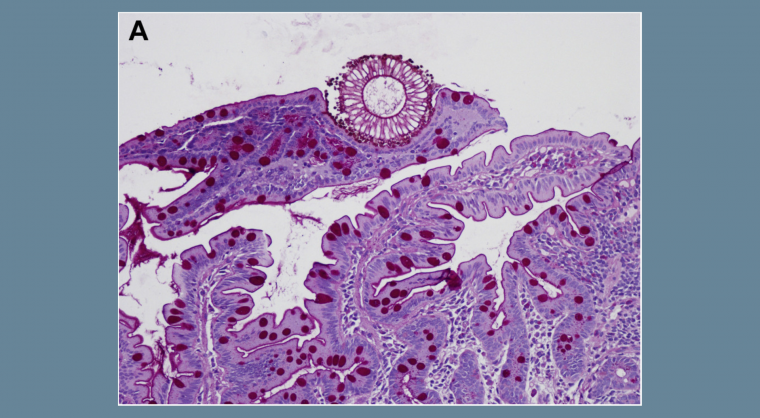
Colonoscopy showed pancolitis with continuous diffuse granular and friable mucosa (Mayo Score of 2) and upper endoscopy showed antral gastritis and diffuse duodenitis with nonbleeding erosions. The patient was started on steroids (1 mg/kg) followed by the amelioration of diarrhea, but persistence of mild grade fever and vomiting. Histologic examination showed crypt distortions and abscesses associated with goblet cell depletion. An upper endoscopy showed a normal esophageal and gastric mucosa. Duodenal histology (periodic acid–Schiff staining method) is presented in Figure A.
What is the correct diagnosis?